Africa is one of the largest continents in the world with over 50 different countries. It is subdivided into various regions: Northern Africa which is constituted by countries like Egypt, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya; the western region of Africa include countries like Nigeria, Ghana, Mali, Niger, Togo etc.
Countries that occupy the eastern part of Africa include Kenya, Ethiopia, Somalia, Tanzania etc and, Central Africa is made up of countries like Democratic Republic of Congo, Angola, Cameroon, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea etc.
Countries in South Africa is the part that often brings confusion. There are several countries in Southern Africa just like in every other African region. Such countries include Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, Swaziland and South Africa (which is a country within southern Africa).
A lot of people often think that South Africa has other countries within it; but that’s not true, South Africa is the main hub among the Southern African countries.
South Africa is just one country in the southern part of Africa. Geographically, Lesotho is an African country located right inside South Africa forming an enclave (an independent country that is completely landlocked by another) and is the only independent African country to have such attribute. Apart from Lesotho, there are only 2 more landlocked nations in the world – The Republic of San Marino which is enclaved within Italy and The Vatican City, which is enclaved within the city of Rome.
Classification of Countries in South Africa
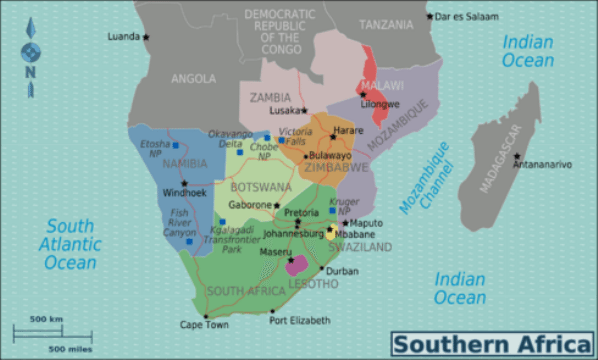
There are 2 major classifications for countries in Southern Africa
The United Nations classification and that of the Southern African Development Community (SADC) which is an inter-governmental agency headquartered in Gaborone, Botswana with the sole purpose of fostering socio-economic integration and growth among the member states. One may consider it as a smaller version of the African Union.
United Nations Recognition of Countries in South Africa
According to the United Nations, there are 5 different countries that make-up Southern Africa. They include:
1. South Africa
2. Namibia
3. Lesotho
4. Botswana
5. Swaziland
These countries constitute the geographic mapping of South African countries according to the United Nations. This is also the classification used by the Southern African Customs Union (SACU) which was established in 1969 to replace the customs union of 1910 making it the oldest existing customs union in the world.
Southern African Development Community (SADC) Classification of South African Countries
According to Southern African Development Community (SADC), 15 countries constitute the South African region. The countries include the following:
1. Angola
2. Namibia
3. Mozambique
4. Tanzania
5. Swaziland
6. Seychelles
7. South Africa
8. Mauritius
9. Zambia
10. Zimbabwe
11. Botswana
12. The Democratic Republic of the Congo
13. Lesotho
14. Madagascar
15. Malawi
Sometimes, the 2 major islands (Madagascar and Mauritius) are regarded as countries in East Africa.
See Also: Tribes of South Africa
The Economy of South African Region
Southern Africa is endowed with natural resources like gold, platinum and diamond but just like other countries in Africa, corruption and the bane of colonialism has shaped this region into what it is today.
Among all the countries in Southern Africa, South Africa is the economic superpower, the main centre of economic activity and development. South Africa’s GDP is more than those of all other countries in this region put together.
Southern African People, History and Culture
Various countries in South Africa have various people who adopt different cultures. Through the years of migration, colonization, and resettlement in Southern African history, the cultures of this region have changed quite a lot resulting in a significant population of European (Afrikaners, Anglo-Africans, Portuguese Africans, etc.) and Asian descent (Cape Malays, Indian South Africans, etc.) in many southern African countries.
The Bantu expansion pushed the former occupants of the region to the more remote areas and this is the reason most of the ethnic groups in this region speak languages which share common Bantu language origin and include the people of Zulu, Xhosa, Northern Ndebele, Swazi, Ovimbundu, Chaga, Southern Ndebele, Tswana, Sotho, Balunda, Mbundu, Sukuma and Shona.
